What is the Balanced Scorecard?
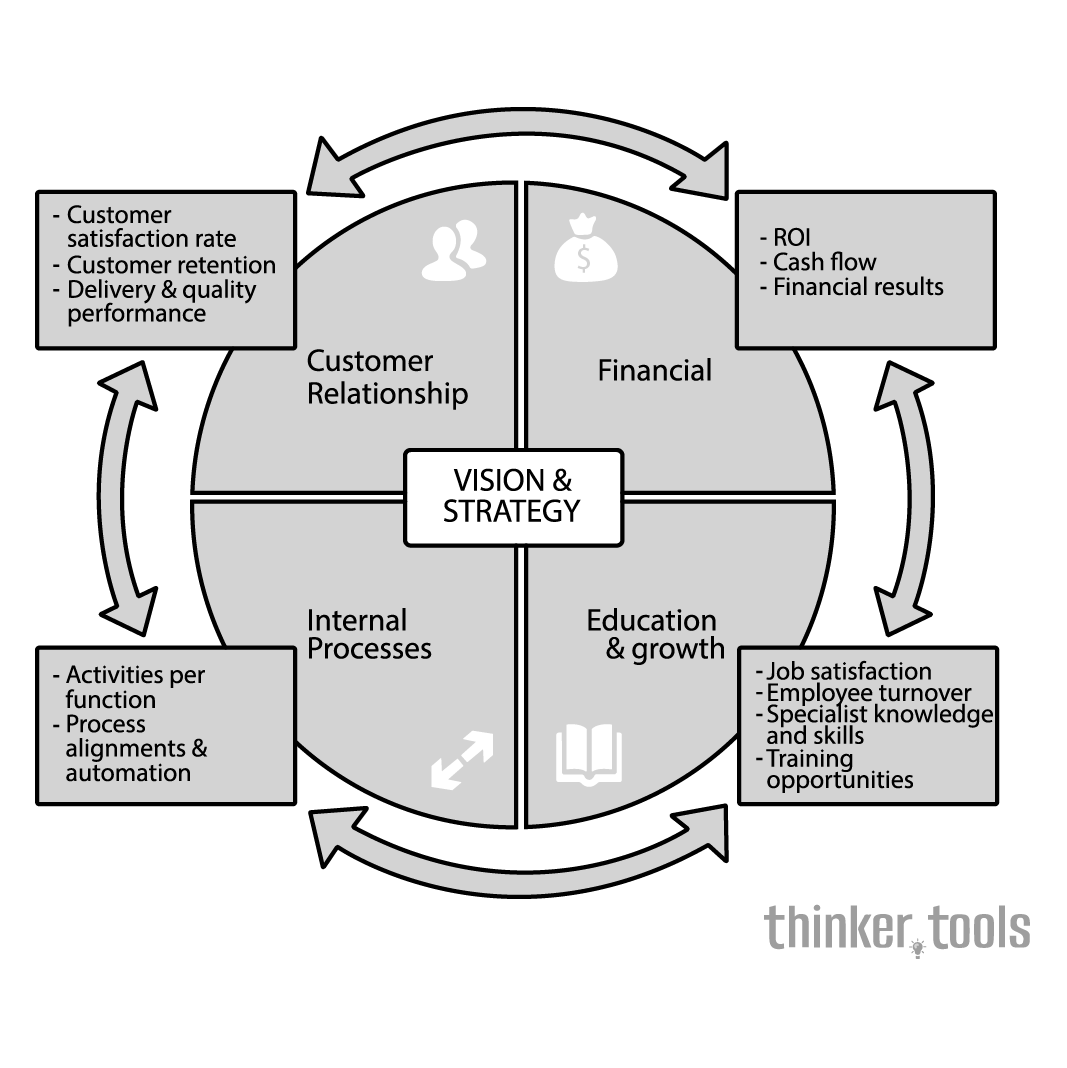
The Balanced Scorecard is a performance measurement framework that adds strategic non-financial performance measures to traditional financial metrics. It provides managers and executives with a more comprehensive view of organizational performance by examining the business from four perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Business Processes, and Learning & Growth.
History and Origin
Developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton in the early 1990s, the Balanced Scorecard emerged from a year-long research project involving 12 companies. The researchers discovered that traditional financial accounting measures were insufficient for guiding and evaluating organizations in the information age. Their groundbreaking Harvard Business Review article "The Balanced Scorecard—Measures that Drive Performance" (1992) introduced this revolutionary concept to the business world.
How to Use the Balanced Scorecard: Step by Step
Step 1: Define Your Vision and Strategy
Start by clearly articulating your organization's vision and strategic objectives. What do you want to achieve in the long term? What is your competitive strategy?
Step 2: Develop the Four Perspectives
Financial Perspective: Define how you look to shareholders. Common metrics include revenue growth, profitability, return on investment, and economic value added.
Customer Perspective: Determine how customers see you. Focus on customer satisfaction, retention, market share, and customer acquisition.
Internal Process Perspective: Identify what you must excel at internally. Look at operational efficiency, quality, innovation processes, and regulatory compliance.
Learning & Growth Perspective: Assess your ability to improve and create value. Consider employee training, corporate culture, knowledge management, and information systems.
Step 3: Create Strategic Objectives
For each perspective, develop 3-5 strategic objectives that support your overall strategy. These should be specific, measurable goals that cascade throughout the organization.
Step 4: Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Define metrics for each strategic objective. These KPIs should be quantifiable and directly linked to your strategic goals.
Step 5: Set Targets and Initiatives
Establish specific targets for each KPI and identify initiatives or projects that will help achieve these targets.
Step 6: Monitor and Review
Regularly review performance against targets, analyze variances, and adjust strategies as needed. The Balanced Scorecard is a living document that should evolve with your organization.
Practical Examples
Healthcare Organization Example:
- Financial: Reduce operating costs by 10% while maintaining quality
- Customer: Achieve 95% patient satisfaction scores
- Internal Process: Reduce patient wait times to under 30 minutes
- Learning & Growth: Train 100% of staff in new electronic health records system
Technology Startup Example:
- Financial: Achieve $5M in annual recurring revenue
- Customer: Maintain Net Promoter Score above 70
- Internal Process: Reduce software deployment time by 50%
- Learning & Growth: Hire 10 senior engineers and establish mentorship program
Benefits and Life Improvements
The Balanced Scorecard framework offers numerous benefits that can significantly improve organizational and personal effectiveness:
Strategic Alignment: It ensures that all organizational activities are aligned with the overall strategy, reducing wasted effort and conflicting priorities.
Improved Communication: The framework provides a common language for discussing strategy throughout the organization, from the boardroom to the front lines.
Better Decision Making: By considering multiple perspectives, leaders make more informed decisions that balance short-term pressures with long-term sustainability.
Enhanced Performance: Organizations using the Balanced Scorecard typically see improved financial performance, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
Personal Application: Individuals can adapt the framework for personal goal setting, balancing financial goals, relationships, personal development, and health objectives.
The Balanced Scorecard transforms abstract strategy into concrete actions and measurable outcomes. By providing a holistic view of performance, it helps organizations navigate complexity, adapt to change, and achieve sustainable success. Whether you're leading a multinational corporation or managing your personal goals, the Balanced Scorecard offers a proven framework for turning vision into reality.