What is the COSO Cube?
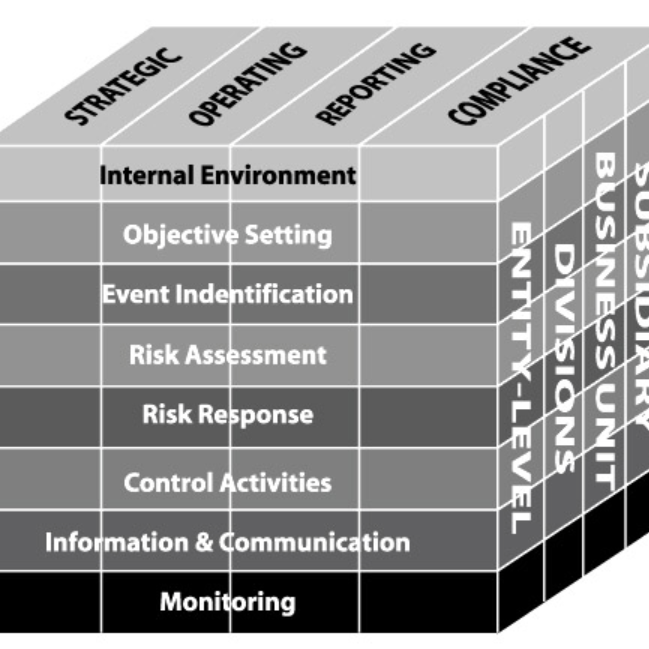
The COSO Cube is a three-dimensional framework that visualizes the relationship between an organization's objectives, its organizational structure, and the components of enterprise risk management. The cube's three dimensions represent: organizational objectives (Strategic, Operations, Reporting, and Compliance), organizational levels (Entity, Division, Business Unit, and Subsidiary), and eight interrelated risk management components. This visual representation helps organizations understand that risk management isn't a linear process but rather a dynamic, multidirectional set of activities.
History and Origin
The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) was formed in 1985 to sponsor the National Commission on Fraudulent Financial Reporting. Following several high-profile corporate failures, COSO recognized the need for a comprehensive risk management framework. The original framework was published in 2004, with a significant update in 2017 to reflect the evolution of risk management and the increasing complexity of business environments. The cube visualization was introduced to help practitioners better understand the multidimensional nature of enterprise risk management.
How to Use the COSO Cube: Step by Step
Step 1: Understand the Three Dimensions
First Dimension - Objectives Categories:
- Strategic: High-level goals aligned with mission
- Operations: Effective and efficient use of resources
- Reporting: Reliability of internal and external reporting
- Compliance: Adherence to laws and regulations
Second Dimension - Organizational Structure:
- Entity Level (entire organization)
- Division
- Business Unit
- Subsidiary/Function
Third Dimension - ERM Components:
- Internal Environment
- Objective Setting
- Event Identification
- Risk Assessment
- Risk Response
- Control Activities
- Information & Communication
- Monitoring
Step 2: Establish the Internal Environment
Create a risk-aware culture by:
- Defining risk philosophy and appetite
- Establishing ethical values and integrity standards
- Setting the organizational structure
- Assigning risk management responsibilities
Step 3: Set Clear Objectives
Align objectives across all categories:
- Ensure objectives support the organizational mission
- Make objectives measurable and time-bound
- Consider risk tolerance for each objective
- Cascade objectives throughout organizational levels
Step 4: Identify Potential Events
Systematically identify events that could impact objectives:
- Use techniques like brainstorming, interviews, and process analysis
- Consider both internal and external factors
- Document both risks (negative events) and opportunities (positive events)
- Create a comprehensive risk inventory
Step 5: Assess Identified Risks
Evaluate risks based on:
- Likelihood of occurrence
- Potential impact on objectives
- Inherent risk (before controls)
- Residual risk (after controls)
- Use both qualitative and quantitative methods
Step 6: Formulate Risk Responses
Develop strategies for each significant risk:
- Accept: Acknowledge risk and take no action
- Avoid: Exit activities that create risk
- Reduce: Implement controls to mitigate
- Share: Transfer portion of risk (insurance, partnerships)
Step 7: Implement Control Activities
Design and execute controls:
- Preventive vs. detective controls
- Manual vs. automated controls
- Management review and approval processes
- Physical controls and segregation of duties
Step 8: Ensure Information Flow and Communication
Establish systems for:
- Capturing relevant risk information
- Communicating vertically and horizontally
- External stakeholder communication
- Real-time risk reporting dashboards
Step 9: Monitor and Improve
Continuously evaluate the ERM system:
- Ongoing monitoring activities
- Separate periodic evaluations
- Internal audit reviews
- Implement improvements based on findings
Practical Examples
Manufacturing Company Example:
- Strategic Objective: Expand into Asian markets
- Risk Identified: Supply chain disruption
- Assessment: High likelihood, severe impact
- Response: Diversify suppliers, maintain strategic inventory
- Controls: Supplier audits, real-time tracking systems
- Monitoring: Monthly supply chain risk metrics
Financial Services Example:
- Compliance Objective: Meet new data privacy regulations
- Risk Identified: Data breach and regulatory penalties
- Assessment: Medium likelihood, severe impact
- Response: Reduce through enhanced cybersecurity
- Controls: Encryption, access controls, employee training
- Monitoring: Quarterly security assessments
Healthcare Organization Example:
- Operational Objective: Reduce patient wait times by 30%
- Risk Identified: Staff burnout leading to turnover
- Assessment: High likelihood, moderate impact
- Response: Share risk through staffing partnerships
- Controls: Workload monitoring, wellness programs
- Monitoring: Monthly staff satisfaction surveys
Benefits and Life Improvements
The COSO Cube framework delivers transformative benefits for organizations and individuals:
Holistic Risk Perspective: The three-dimensional view ensures no aspect of risk is overlooked, creating comprehensive protection for organizational value.
Strategic Alignment: By linking risk management to objectives, organizations ensure that risk-taking is purposeful and aligned with strategy.
Improved Decision Making: Better risk information leads to more informed decisions at all organizational levels.
Enhanced Accountability: Clear assignment of risk ownership improves accountability and response effectiveness.
Regulatory Compliance: Many regulators recognize COSO, making compliance more straightforward for organizations using the framework.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations with mature risk management often outperform peers by avoiding pitfalls and capitalizing on opportunities.
Cultural Transformation: Implementing COSO often creates a more risk-aware, proactive organizational culture.
Personal Applications: Individuals can apply COSO principles to personal risk management—financial planning, career decisions, and life choices—using the same systematic approach.
The COSO Cube transforms risk management from a compliance exercise into a strategic capability. Its three-dimensional approach ensures that organizations consider risk from multiple perspectives, creating a more resilient and agile enterprise. Whether you're managing risks for a global corporation or planning your personal finances, the COSO framework provides a structured approach to navigating uncertainty while pursuing ambitious objectives. By embracing this comprehensive framework, organizations and individuals can turn risk management from a defensive necessity into an offensive advantage.