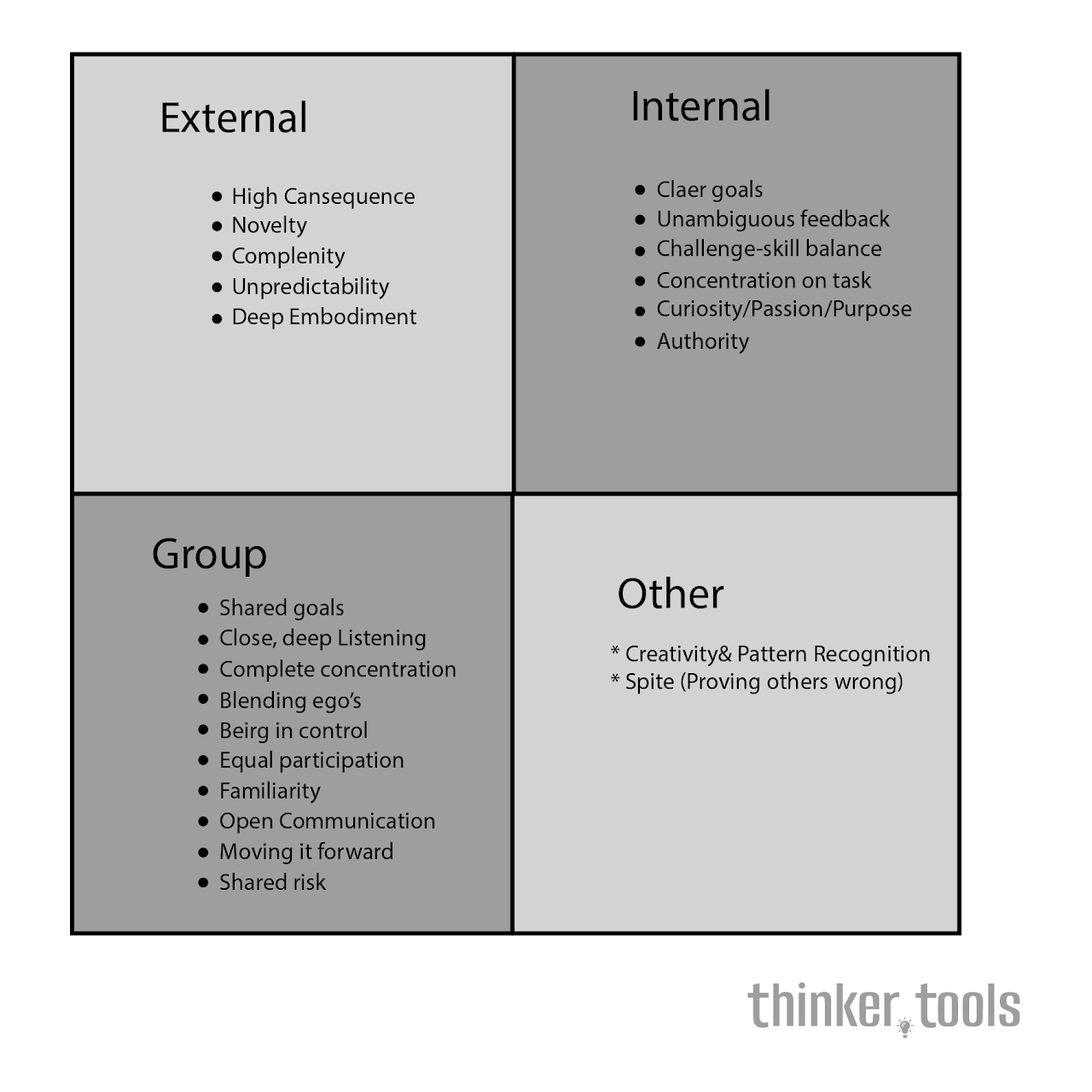
What are Flow Triggers?
Flow triggers are conditions that drive attention into the present moment and push us toward the flow state—that optimal experience where we feel and perform our best. Researchers have identified 22 flow triggers across four categories:
- Psychological triggers: Internal conditions like clear goals and immediate feedback
- Environmental triggers: External conditions like high consequences and rich environments
- Social triggers: Group dynamics like shared goals and close listening
- Creative triggers: Activities that blend novelty with familiarity
These triggers work by driving focus, increasing neurochemical rewards, and creating the perfect challenge-to-skill ratio.
The History and Origin
The concept of flow was first identified by psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi in the 1970s through extensive research on optimal experience. However, the systematic study of flow triggers emerged from the work of Steven Kotler and the Flow Research Collective in the 2000s. By analyzing extreme athletes, top executives, and creative artists, researchers decoded the specific conditions that reliably produce flow states, transforming what was once considered mystical into practical science.
How to Use Flow Triggers: Step by Step
Step 1: Master the Psychological Triggers
Clear Goals Set specific, immediate objectives for each work session. Your brain needs to know exactly what success looks like.
Immediate Feedback Structure activities to provide constant feedback on performance. This keeps your attention locked in the present.
Challenge-Skill Balance Aim for tasks that are 4% beyond your current ability—challenging enough to demand focus, but not so hard they cause anxiety.
Deep Concentration Eliminate distractions and create uninterrupted blocks of time for deep work.
Step 2: Optimize Environmental Triggers
High Consequences Add stakes to your performance—deadlines, public commitments, or meaningful outcomes that matter.
Rich Environments Work in spaces with novelty, unpredictability, and complexity that demand attention.
Deep Embodiment Engage multiple senses and include physical movement when possible.
Step 3: Leverage Social Triggers
Shared Goals Align with others toward a common objective to amplify collective focus.
Equal Participation Ensure everyone contributes equally to maintain group flow.
Familiar Communication Develop shared language and understanding that enables effortless collaboration.
Close Listening Practice intense presence and attention to others' contributions.
Step 4: Incorporate Creative Triggers
Novelty Introduce new elements regularly to keep your brain engaged and pattern-seeking.
Unpredictability Build in surprise and variation to maintain attention.
Pattern Recognition Engage in activities that involve finding connections and solving puzzles.
Step 5: Stack Your Triggers
The more triggers you can activate simultaneously, the more likely you'll enter flow. Design your work to incorporate multiple triggers.
Step 6: Track and Refine
Keep a flow journal noting which triggers work best for you in different contexts. Refine your approach based on results.
Practical Examples
Example 1: The Writer's Flow Stack
- Clear Goals: Write 1,000 words on a specific topic
- Immediate Feedback: Word count visible, writing app provides progress bar
- High Consequences: Public commitment to daily publishing
- Rich Environment: Writing in a new café each day
- Deep Embodiment: Standing desk, background music engaging multiple senses
Example 2: The Programmer's Peak Performance
- Challenge-Skill Balance: Tackling a bug that's just beyond current knowledge
- Deep Concentration: Phone in another room, all notifications off
- Immediate Feedback: Code compiles or fails instantly
- Pattern Recognition: Debugging requires finding hidden connections
- Novelty: Using a new framework or approach
Example 3: The Team's Collective Flow
- Shared Goals: Launching product feature by sprint end
- Equal Participation: Daily standups where everyone contributes
- Familiar Communication: Established team terminology and inside jokes
- Close Listening: Pair programming sessions with intense collaboration
- High Consequences: Customer demo scheduled for sprint review
Example 4: The Athlete's Training Zone
- Deep Embodiment: Full-body engagement in movement
- Immediate Feedback: Times, distances, form corrections
- Challenge-Skill Balance: Training at 104% of previous performance
- High Consequences: Upcoming competition
- Unpredictability: Varied training environments and conditions
Benefits and Life Improvements
Exponential Performance Gains
Research shows that people in flow are up to 500% more productive. Flow triggers help you access this state consistently, transforming your output and impact.
Accelerated Learning
The neurochemical cocktail released during flow enhances pattern recognition and memory formation. You learn faster and retain more.
Increased Creativity
Flow states produce a 200-700% boost in creative problem-solving. Regular flow makes innovation your default mode.
Enhanced Well-being
Flow is intrinsically rewarding, producing the same neurochemicals as love and recreational drugs—but naturally and sustainably.
Reduced Burnout
Working in flow feels effortless despite high performance. You accomplish more while feeling less stressed and depleted.
Deeper Fulfillment
Flow states are consistently rated as life's most meaningful experiences. More flow equals a richer, more satisfying life.
Career Advancement
Professionals who regularly access flow outperform their peers dramatically, leading to faster advancement and greater opportunities.
Activate Your Flow Potential
Flow triggers transform peak performance from accident to method. By understanding and systematically applying these triggers, you can make your best moments your most common moments. Start by identifying which triggers resonate most with your work style and context. Experiment with one or two triggers at first, then gradually build your flow stack.
Remember, flow is a skill that improves with practice. Each time you successfully trigger flow, you strengthen the neural pathways that make future flow states easier to access. What once required perfect conditions becomes available on demand. Your potential for excellence isn't limited by talent or circumstances—it's unlocked by understanding and applying the science of flow triggers. Begin today, and watch as your work transforms from struggle to effortlessness, from good to extraordinary.